How to Prevent Escherichia coli O157:H7
Escherichia coli O157:H7 is surfacing and threatening USA and Canada, especially ham and other processed meat products sold in supermarkets and convenience stores.
What is O157:H7?
Escherichia coli is a bacterium that is commonly found in the intestine of animals. Most E. coli strains are harmless, but there exist, such as serotype O157:H7 that can cause serious food poisoning among people. This is a strain of E. coli that became notorious in Japan and responsible for several mass food poisonings in the country.
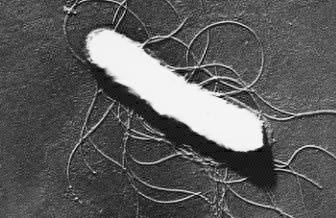
Selected Escherichia coli O157:H7 Outbreaks
Below are some reported E. coli O157:H7 outbreaks in Japan, USA, and Canada.
1982: Hamburger food poisoning occurred in Oregon and Michigan, USA.
1984: Hemorrhagic enteritis occurred in Osaka and Tokyo, Japan, and found a strain of E. coli O157:H7.
1990: In Saitama, Japan, the Urawa Kindergarten water well was contaminated with E. coli O157:H7. Two students died.
1996 July 13: In my hometown in Sakai City, Osaka, Japan, schoolchildren were infected from canteen lunches. 7,996 patients were hospitalized after eating contaminated radish sprouts, and three students died.
1996: In Okinawa, Japan, a school lunch was contaminated with E. coli O157:H7, and almost at the same time, the Japanese Ministry of Health found the same in Okayama.
2005: In a public nursing home in Kagawa, Japan, E. coli O157:H7 infection was found from the marinade products. In the same year, an outbreak also occurred in Osaka due to a contaminated lunch food.
2005 November 23: In Takatsuki, Osaka where my brother lives, a 13 year-old infant was hospitalized and detected a strain of E. coli O157:H7. He died after a few days.
2006: In Kagawa, Japan, E. coli O157:H7 was again detected from marinade products.
2006 North American E. coli outbreak: In September 2006, E. coli O157:H7 was found in uncooked spinach cultivated in California. Report indicates 26 U.S. states were affected and 199 people had been infected. Three people died and 31 people suffered from a type of kidney failure. In December 2006, another outbreak occurred across five states involving lettuce, 52 of whom have been tested positive from the same E. coli strain.
2007 May 28: In Tokyo, Japan, about 54 students In Musashino University were infected by E. coli O157:H7 from food served in the school cafeteria. The students suffered from diarrhea with nausea and food poisoning symptoms.
2008 July-August: Sausage and ham sold in several convenience stores in Canada and USA was infected with E. coli O157:H7. Many people who ate without heating them were affected.
Escherichia coli is not always confined to the intestine. It also has the ability to live for brief periods outside the body. It is the reason that you can get some samples from raw meat, fresh vegetables, and water for investigation. Remember that inadequate heating or reheating of raw meats, vegetables, and water can cause the bacteria to grow that will lead to food poisoning.
Some scientists believe that E. coli O157:H7 is also associated with virus, and I believe that this is very true.
The bacteria produce verotoxin (a.k.a. Shiga-like toxin). The verotoxin acts on the lining of the blood vessels, especially the small blood vessels like those found in the digestive tract where it is most effective. The toxin binds and enters to a component of the cell membrane and breaks protein synthesis, thus, leading to the death of the cell. This will cause severe abdominal pain and commonly a bloody diarrhea. The toxin also destroys the filtering structure of the kidney leading to kidney failure. Hemolytic-uremic syndrome and acute encephalopathy that may lead to death can occur, too.
How to Prevent the Spread of E. coli O157:H7
Slaughterhouses are responsible for preventing E. coli O157:H7 from their infected cattle. One problem is the cattle may not show any symptoms of the infection. Cattle droppings should be inspected as well.
Heating raw materials and foods such as hamburger, sausage, and ham at temperature of 75 °C (167 °F) for at least one minute will help prevent E. coli O157:H7.
In addition, raw liver and pasteurized foods are not recommended for children as well as elderly people.
Although medical sciences of today and our findings about E. coli O157:H7 do not correspond most of the time, we just believe that E. coli O157:H7 related symptoms are not only caused by bacteria but also complicated with the negative energy. Just like BSE (bovine spongiform encephalopathy), commonly known as Mad Cow Disease, medical scientists had believed that foods contaminated with viruses are the source of BSE. Today, we received information from U.S. medics that the DNA of the disease was found from a newly born cow. This means that heredity is one of the causes of BSE. As I mentioned several years ago, BSE is caused by the negative energy. Soon you will believe what I said.
Reprint Rights: You may reprint this article within your website, blog, or newsletter as long as the entire article remains the same as well as the “About the Author” box.



 Junji Takano is a Japanese health researcher involved in investigating the cause of many dreadful diseases. In 1968, he invented PYRO-ENERGEN, the first and only electrostatic therapy machine that effectively eradicates viral diseases, cancer, and diseases of unknown cause.
Junji Takano is a Japanese health researcher involved in investigating the cause of many dreadful diseases. In 1968, he invented PYRO-ENERGEN, the first and only electrostatic therapy machine that effectively eradicates viral diseases, cancer, and diseases of unknown cause.


